Quick Start
OpenRun is an Apache-2.0 licensed project building a web app development and deployment platform for internal tools. OpenRun is built in Go and runs on Linux, macOS and Windows.
Installation
Install OpenRun On OSX/Linux
To install on OSX/Linux, run
curl -sSL https://openrun.dev/install.sh | shStart a new terminal (to get the updated env) and run openrun server start to start the OpenRun service.
Brew Install
To install using brew, run
brew tap openrundev/homebrew-openrun
brew install openrun
brew services start openrunInstall On Windows
To install on Windows, run
powershell -Command "iwr https://openrun.dev/install.ps1 -useb | iex"Start a new command window (to get the updated env) and run openrun server start to start the OpenRun service.
Install Apps
Once OpenRun server is running, to install apps declaratively, open a new window and run
openrun apply --approve github.com/openrundev/openrun/examples/utils.starTo install apps using the CLI, run
openrun app create --approve github.com/openrundev/apps/system/list_files /files
openrun app create --approve github.com/openrundev/apps/system/disk_usage /disk_usage
openrun app create --approve github.com/openrundev/apps/utils/bookmarks /bookOpen https://localhost:25223 to see the app listing. The disk usage app is available at https://localhost:25223/disk_usage (port 25222 for HTTP). The bookmark manager is available at https://localhost:25223/book, the list files app is available at https://localhost:25223/files.
The release binaries are also available at releases.
Application Types
OpenRun allows easy management of multiple apps on one OpenRun server installation. There are three main types of OpenRun apps:
- Action apps - App backend is defined in Starlark and an auto generated form UI and report is created by OpenRun. These are the simplest apps.
- Containerized Apps - App backend (in any language/framework) runs in a container. OpenRun acts as an application server doing reverse proxying for the app APIs. This allows OpenRun to install and manage apps built in frameworks like Streamlit/Gradio/FastHTML/FastAPI/Flask etc.
- Hypermedia apps - The app is completely customizable, allowing combining containerized apps with actions and custom API handlers, building Hypermedia driven UIs.
For all apps, OpenRun provides blue-green staged deployment, OAuth access controls, secrets management, TLS cert management etc.
Action Apps
For use cases where an existing CLI application or API needs to be exposed as a web app, actions provide an easy solution. First, define the parameters to be exposed in the form UI. Create a params.star file with the params. For example,
param("dir", description="The directory to list files from", default="/tmp")The app defines a run handler which runs ls on the specified directory. The output text is returned.
load ("exec.in", "exec")
def run(dry_run, args):
out = exec.run("ls", ["-Lla"]).value
return ace.result("File listing for " + args.dir, out)
app = ace.app("List Files",
actions=[ace.action("List Files", "/", run, description="Show the ls -a output for specified directory")],
permissions=[
ace.permission("exec.in", "run", ["ls"]),
],
)The app, when accessed will look as shown below, with the ls command output displayed:
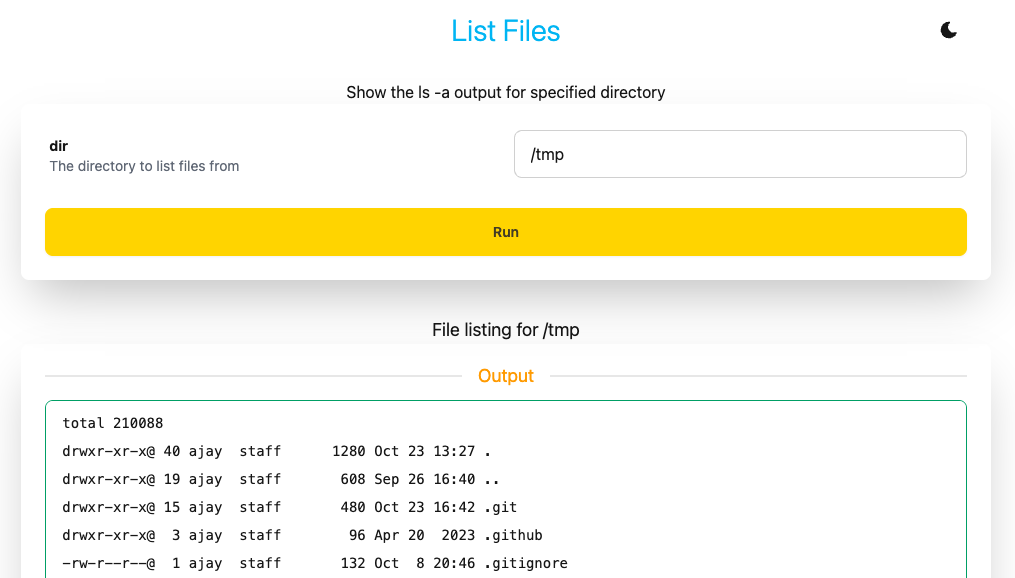
See list files code:demo for the above app. See dictionary code:demo for another actions example app which shows different type of reports. Actions has more details on building app actions.
Containerized Applications
OpenRun apps which are implemented in Starlark run within the OpenRun server. No containers are required for running those apps. For apps where the backend is implemented in any other language, containers are used to run the app. OpenRun works with Docker and Podman. By default, the server looks for the podman client CLI. If not found, it looks for the docker client CLI. To customize this, add in server config
[system]
container_command = "/path/to/container_manager_cli"There are two options for using containerized apps. One is to include the required files in the app repo. This will mean there should be app.star with the app config, a Containerfile or Dockerfile with the container config. The other option is to use an app spec. This allows you to use OpenRun without requiring any changes to your app. No container file is even required. For example, the command
openrun app create --spec python-streamlit --branch master --approve \
github.com/streamlit/streamlit-example /streamlitdoes the following:
- Checks out the
github.com/streamlit/streamlit-example - Copy any missing files from the app specification
python-streamlitinto the repo - Load the app source and metadata into the OpenRun server metadata database (SQLite)
When the first API call is done to the app (lazy-loading), the OpenRun server will build the container image from the Containerfile defined in the spec, start the container and set up the proxy for the app APIs.
Any env params which need to be passed to the app can be configured as app params. Params are set during app creation using app create --param port=9000 or after creation using param update port 9000 /myapp.
If the source repo has a Containerfile or Dockerfile, the container spec is a generic spec which works with any language or framework. If the container file defines a port using the EXPOSE directive, then port is not required. Otherwise, specify a port, for example
openrun app create --spec container --approve --param port=8000 \
github.com/myorg/myrepo /myappSee containerized apps for details.
Managing Applications
Multiple applications can be installed on an OpenRun server. Each app has a unique path and can be managed separately. The app path is made up of domain_name:url_path. If no domain_name is specified during app creation, the app is created in the default domain. The default domain is looked up when no specific domain match is found. See app routing for details about routing.
For local env, URL-based routing can be used or *.localhost domain can be used for domain-based paths. For production deployment, if wildcard DNS is set up, domain-based routing can be used without new DNS entries being required per app. Apps can be hosted on multiple unrelated domains on one OpenRun server.
App Installation
To install apps, run openrun app create --approve <source_url> <[domain:]app_path>. For example,
openrun app create --approve github.com/openrundev/apps/system/disk_usage /disk_usageThis is installing the system/disk_usage app from the main branch of the openrundev/apps repo on GitHub. The app is installed for the default domain, to the /disk_usage path. Opening https://127.0.0.1:25223/disk_usage will initialize the app and show the app home page.
/disk_usage/* path is now reserved for APIs under this app. No new apps can be installed under the /disk_usage/ path, but /disk_usage2 is available. Similarly, installing an app under / path means no new apps can be installed for the default domain.If the app code is available on the OpenRun server node, the app create can be done directly with the local disk path:
openrun app create --approve ./diskapp /disk_usage_localWhen developing an app, the source code for the app has to be present locally. To install an app in dev mode, add the --dev option.
openrun app create --dev --approve ./diskapp /disk_usage_devIf an app is created in dev mode with git as the source path, the git repo is checked out automatically into $OPENRUN_HOME/app_src and the app is created from the local source.
In dev mode, source code changes are picked up immediately and the app is live reloaded. For non-dev (prod) apps, app reload has to be done to pick up changes, from local disk or from git.
openrun app reload --approve --promote "/disk_usage*"For apps created from GitHub source, app reload will pick up the latest changes from the branch specified during app create (default is main). For apps created from local disk sources, the reload loads from the folder originally used during the create. For non-dev apps, the source code is loaded into the SQLite metadata database managed by the OpenRun server. This allows for versioning, even when working with local sources.
App Security
Application config is specified in Starlark code in the app.star file. By default, the app does not have any permissions. All external actions an app can perform are done through plugin API calls. Every plugin API call needs to be approved before it is allowed. This allows for multiple apps to run on the OpenRun server without interfering with each other.
To approve an app’s permissions, run
openrun app approve /disk_usageThe --approve option can be specified during the app create and app reload command to automatically approve the permissions.
Staged Deployments
For dev mode apps, there is just one app. For a prod mode app, creating the app creates a staging app and the actual production app. All config and code changes are applied on the staging mode app first, and then manually promoted using app promote. Promotion is automatic if --promote option is specified for the app reload (or any other command performing a metadata change).
The app list command lists all the apps for the specified glob pattern. By default, it lists only the dev and prod apps. To list the staging apps also, add the --internal (or -i) option to app list. all is a shortcut for *:**, which means all apps in all domains. all is the default for app list. For example:
openrun app list --internal alllists all the apps and internal apps for each app. openrun app list "example.com:**" lists the main apps for the example.com domain.
The staging app can be used to verify whether changes are working before the production app is updated. The staging app is accessible by suffixing _cl_stage at the end of the prod app path. So for an app at https://example.com/, the staging url is https://example.com/_cl_stage. For an app at /utils/app1, the staging app url is /utils/app1_cl_stage.
To promote changes from staging to prod, run:
openrun app promote allor openrun app promote "/disk_usage*" to promote specific apps. Use the --dry-run option to verify commands before they are actually applied.
Lifecycle without Git
If not using git, a workflow would be:
- Create a dev mode app, like
openrun app create --dev --approve ~/myappcode /myapp_dev - Create a prod mode app, like
openrun app create --approve ~/myappcode /myapp - As code changes are saved to disk, the changes are immediately live at
https://localhost:25223/myapp_dev - When code is in a stable state, run
openrun app reload /myapp. This will update the staging app with the most recent code from~/myappcodefolder. - The staging app is available at
https://localhost:25223/myapp_cl_stagefor verification. - To promote the code to prod, run
openrun app promote /myapp. The staged code is promoted to prod, live athttps://localhost:25223/myapp.
Having a staging environment helps catch code and config issues before the changes are live on prod. OpenRun implements versioning for prod apps, even when source is not from git.
Lifecycle With Git
If using git, a workflow would be:
- Create a dev mode app, like
openrun app create --dev --approve ~/myappcode /myapp_dev - Create a prod mode app, like
openrun app create --approve github.com/myorg/repo /myapp - As code changes are saved to disk, the changes are immediately live at
https://localhost:25223/myapp_dev - When code is in a stable state, check in the dev code to git.
- Run
openrun app reload /myapp. This will update the staging app with the most recent code frommainbranch in git. - The staging app is live at
https://localhost:25223/myapp_cl_stage. Verify the functionality of the staging app. - To promote the code to prod, run
openrun app promote /myapp. The staged code is promoted to prod, live athttps://localhost:25223/myapp.
App Listing
Use openrun app list to get list of installed app. By default, all apps are listed. Use a glob pattern like example.com:** to list specific apps. Pass the --internal or -i option to list to include the internal apps in the app listing. The pattern matches the main apps, and if the internal option is specified, the matched app’s linked apps are also listed.
Use openrun version list to get list of versions for an app. openrun version switch allows switching between versions. The version command can be run separately on the staging app and prod app, like openrun version list /myapp_cl_stage and openrun version list /myapp. The current version is indicated in the output.
$ openrun version list /dugit
Active Version Previous CreateTime GitCommit GitMessage
1 0 2024-02-16 19:39:05 +0000 UTC 03ccaa35927667977646 Added version file listing support
2 1 2024-02-16 19:55:51 +0000 UTC 03ccaa35927667977646 Added version file listing support
=====> 3 2 2024-02-16 21:18:16 +0000 UTC c00d7b1e99712de13745 Added version switching support
$ openrun version list /dugit_cl_stage
Active Version Previous CreateTime GitCommit GitMessage
1 0 2024-02-16 19:39:05 +0000 UTC 03ccaa35927667977646 Added version file listing support
2 1 2024-02-16 19:54:22 +0000 UTC 03ccaa35927667977646 Added version file listing support
3 2 2024-02-16 20:38:44 +0000 UTC c00d7b1e99712de13745 Added version switching support
=====> 4 3 2024-02-16 21:18:42 +0000 UTC c00d7b1e99712de13745 Added version switching support
$ openrun app list -i /dugit
Id Type Version Auth GitInfo Domain:Path SourceUrl
app_prd_2cSkPeHiATfH46pcUX8EdZqdWQb PROD* 3 SYST main:c00d7b1e99712de13745 /dugit github.com/openrundev/openrun/examples/disk_usage
app_stg_2cSkPeHiATfH46pcUX8EdZqdWQb STG 4 SYST main:c00d7b1e99712de13745 /dugit_cl_stage github.com/openrundev/openrun/examples/disk_usageIn the above listing, the staging app is on version 4, prod app on version 3. The * in the app list output indicates that the prod app has staged changes waiting to be promoted. Running openrun app promote /dugit will update prod with the staged changes. version revert reverts to previous version. version switch can be used to switch to particular version, next and previous are shortcuts for version numbers. Version commands run against the specific app, so revert can be done on the staging app or the main app independently.
Developing Apps
OpenRun app backend can be written in any language, running in a container. Action and Hypermedia based apps can be written in Starlark and Go HTML templates, in which case no containers are required.
See develop for a quick start overview on developing OpenRun applications.